
Call 0330 880 3600 Calls may be monitored or recorded. Opening Times.
- TRAVEL INSURANCE
- COVID-19 ENHANCED COVER
- More Options
- Help & Advice
- Existing Customers

Call 0330 880 3600 Calls may be monitored or recorded. Opening Times.
Need help?
UK Customer Services0330 880 3600
Open Open Monday to Friday 9:00am to 6pm, Saturday 8:30am to 4pm and closed Sundays.
(Calls may be monitored or recorded)
Contact details can be found in your policy documentation
Available 24 hours a day, every day

Region: Asia & Oceania
Full Name: People's Republic of China
Capital City: Beijing
Language Spoken: Standard Chinese or Mandarin (Putonghua, based on the Beijing dialect),Yue (Cantonese), Wu (Shanghaiese), Minbei (Fuzhou), Minnan (Hokkien-Taiwanese), Xiang, Gan, Hakka dialects, minority languages (see Ethnic groups entry)
Get travel insurance to China from Direct Travel Insurance. We offer low cost and high quality travel insurance to China and most of the world.

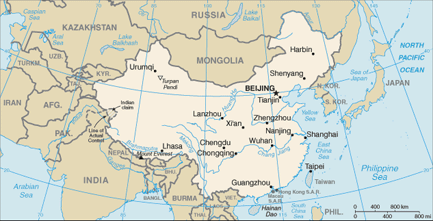
35 00 N, 105 00 E
lowest point: Turpan Pendi -154 m highest point: Mount Everest 8,850 m
total: 22,117 km border countries: Afghanistan 76 km, Bhutan 470 km, Burma 2,185 km, India 3,380 km, Kazakhstan 1,533 km, North Korea 1,416 km, Kyrgyzstan 858 km, Laos 423 km, Mongolia 4,677 km, Nepal 1,236 km, Pakistan 523 km, Russia (northeast) 3,605 km, Russia (northwest) 40 km, Tajikistan 414 km, Vietnam 1,281 km regional borders: Hong Kong 30 km, Macau 0.34 km
frequent typhoons (about five per year along southern and eastern coasts); damaging floods; tsunamis; earthquakes; droughts; land subsidence
coal, iron ore, petroleum, natural gas, mercury, tin, tungsten, antimony, manganese, molybdenum, vanadium, magnetite, aluminum, lead, zinc, uranium, hydropower potential (world's largest)
arable land: 14.86% permanent crops: 1.27% other: 83.87% (2005)
air pollution (greenhouse gases, sulfur dioxide particulates) from reliance on coal produces acid rain; water shortages, particularly in the north; water pollution from untreated wastes; deforestation; estimated loss of one-fifth of agricultural land since 1949 to soil erosion and economic development; desertification; trade in endangered species
China has a great diversity of climates. The northeast experiences hot and dry summers and bitterly cold winters. The north and central region has almost continual rainfall, hot summers and cold winters. The southeast region has substantial rainfall, with semi-tropical summers and cool winters. Central, southern and western China are also susceptible to flooding, China is also periodically subject to seismic activity.\nRequired clothing\nNorth ? heavyweight clothing with boots for the harsh northern winters. Lightweight clothing for summer. South ? mediumweight clothing for winter and lightweight for summer.
time difference: UTC+8 note: despite its size, all of China falls within one time zone
1,313,973,713 (July 2006 est.)
0-14 years: 20.8% (male 145,461,833/female 128,445,739) 15-64 years: 71.4% (male 482,439,115/female 455,960,489) 65 years and over: 7.7% (male 48,562,635/female 53,103,902) (2006 est.)
total: 32.7 years male: 32.3 years female: 33.2 years (2006 est.)
0.59% (2006 est.)
13.25 births/1,000 population (2006 est.)
6.97 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.)
-0.39 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.)
at birth: 1.12 male(s)/female under 15 years: 1.13 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.06 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.91 male(s)/female total population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2006 est.)
total population: 72.58 years male: 70.89 years female: 74.46 years (2006 est.)
1.73 children born/woman (2006 est.)
Personal relationships in business are critical. The Chinese like to deal with "old friends," and it is important for exporters, importers, and investors to establish and maintain close relationships with their Chinese counterparts and relevant government agencies. It is equally important that American exporters encourage strong personal relationships between their Chinese agents or distributors and the buyers and end-users. A web of strong personal relationships will help ensure smoother development of business in China. Foreign companies are not permitted to directly engage in trade in China, with the exception of the direct marketing of a portion of the goods that they manufacture in China. Accordingly, exporters need to use a domestic Chinese agent for both importing into China and marketing within China. Only those trading companies authorized by the central government to handle exports and imports are permitted to sign import and export trade contracts. Over 10,000 Chinese firms have that authority. Some trading firms have begun to represent foreign manufacturers, in arrangements similar to a "manufacturers representative," but these are still in the minority. With careful selection, training and constant contact, exporters can obtain good market representation from a Chinese trading company, many of which are authorized to deal in a wide range of commodities. Some of the larger Chinese companies have overseas offices in countries around the world, as well as multiple branches in China. However, given transportation and communication difficulties, as well as regional peculiarities, most of these trading companies cannot give diversified coverage throughout China. In addition to the trading companies, China is witnessing an explosion in local sales agents who handle internal distribution and marketing. These firms do not necessarily have import/export authority. They may be representative offices of Hong Kong or other foreign trading companies, or domestic Chinese firms with regional or partial national networks, under supervision of the Ministry of Internal Trade. Given China's size and diversity, as well as the lack of agents with wide-reaching abilities, it makes sense to hire several agents to cover different areas, and to be cautious when giving exclusive territories. China can be divided roughly into at least five major regions: the South (Guangzhou), the East (Shanghai), the Beijing-Tianjin region, Central China and the Northeast. A locally incorporated equity or cooperative joint venture with one or more Chinese partners, or a wholly foreign-owned enterprise (WFOE), may be the final step in developing markets for a company's products. Domestic production avoids import restrictions -- including relatively high tariffs -- and provides firms with greater control over both intellectual property and marketing. The role of the Chinese partner in the success or failure of a joint venture cannot be over-emphasized. A good Chinese partner will have the connections to help smooth over red tape and obstructive bureaucrats; a bad partner, on the other hand, can make even the most promising venture fail. Common investor complaints concern conflicts of interest (e.g., the partner setting up competing businesses), bureaucracy and violations of confidentiality. Companies should bear in mind that joint ventures are time-consuming and resource-demanding, and will involve constant and prudent monitoring of critical areas such as finance, personnel and basic operations in order for them to be a success. Some companies prefer to establish a WFOE rather than a joint venture, with a view to retaining greater management control, due to concerns over intellectual property rights (IPR) protection, desire for simplicity, or for other reasons of corporate policy. The law on WFOEs requires that they either provide advanced technology or be primarily export-oriented, and restricts or prohibits them in a number of service and public utility sectors. However, an increasing number of companies find WFOEs, which now account for roughly 20% of all foreign-invested enterprises, to be a viable entry vehicle to the China market, taking much less time and money to set up than a joint venture. Chinese law requires representative offices and foreign-invested enterprises to retain the services of accountants registered in China to prepare for official submission of annual financial statements and other specified financial documents. To date, only Chinese accountants and joint-venture accounting firms may provide these services. However, all the major international public accounting firms have offices in China and operate a thriving practice providing services to foreign firms, from advice on tax matters to assistance in setting up accounting systems and preparation of feasibility studies. Only attorneys licensed in China may appear in court and advise on questions of Chinese law. At present, foreigners are not permitted to qualify to practice Chinese law, nor are foreign law firms permitted to form joint ventures with Chinese lawyers. Registered foreign law firms in China are restricted to advising on the law of their own jurisdictions. Nonetheless, many international law firms, which have had years of experience in doing business in China, are an invaluable source of advice and guidance in setting up ventures, drafting agreements and resolving disputes. Here are some ways in which one can conduct business with culturally acceptable decorum while visiting China: Mandarin, also known as Putonghua or Common Speech, is the official spoken language in China. Depending on where in China you are doing business, other major dialects include Cantonese, Shanghainese, Fukienese, and Hakka. While it isn't expected that Westerners doing business in China should have a mastery of the given language, you'll gain the respect of your Chinese counterparts by making an attempt to utter at least a few of the simplest phrases or words. Though some westerners think they are workaholics, their work ethic pales by comparison to that of the typical Chinese. Until recently, the official workweek in China was six longer-than-normal days (closed Sundays) with no break for lunch. Today, however, many businesses keep 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. hours, with a break from noon to 1:30 p.m. During that time, the enterprises may totally shut down so that employees can go home for lunch a quick xiuxi (a short nap), so plan accordingly when scheduling business appointments or trying to phone a company to make an appointment. To function well in China it is important to understand the principle of "saving face." In China, an individual's reputation and social standing is based on this complex concept. For example, by turning down a dinner invitation to a Chinese associate's home, you are causing that individual to "lose face" simply because you are not available. To save his or her face, as well as to save your own, you must apologize for not being able to accept the invitation, then propose an alternative plan that is palatable to the person who has extended the invitation. Causing someone to lose face, even though unintentional, is a sure way to put a quick halt to business negotiations with not only one individual, but most likely with his or her entire firm as well. Exchanging business cards in China is like shaking hands: It's part of proper business etiquette. If you can, before venturing overseas, have your business cards printed in both English and Chinese. Otherwise, ask your hotel concierge or hotel business center manager if he or she can take care of having your cards reprinted in both languages (preferably using the local dialect). When you present your bilingual business card to a prospective client, make sure the Chinese translation side of your card is facing the recipient. Then, holding the upper corners of the card with the thumb and forefinger of both hands, offer your card to that person. When he or she gives you a business card, receive the card in the same way as you gave yours, and be sure to examine its contents before putting it carefully in your card case for future reference. Simply stashing the card as soon as you receive it will cause your contact to immediately lose face, and will demonstrate ignorance. The Chinese see haste as a sign of suspicious behavior, so be patient in your business negotiations. Business dealings in this Asian country usually take time (and a few visits) before they can be worked out. Think and then speak if you're in conference with a member of the Chinese community. Also, learn to be a good listener. A quick way to lose credibility with your Chinese counterpart is to make an inaccurate statement. Emphasize company teamwork as opposed to individual business plans. The Chinese place a strong emphasis on the need to work together as if you are each part of a well-oiled machine. They tend to identify with the ideas of a firm as a whole, rather that those ideas of just one business associate.
While the crime rate in China is increasing, it remains generally lower than in most western countries. Crimes are usually nonviolent involving petty thefts, with pickpockets and purse-snatchers accounting most incidents targeting foreigners. To cope with the increases in the violent crime that does occur, the Chinese judicial system took a step in early February, when they executed 8 violent criminals after their hearing. It is the custom of the Chinese to perform executions just prior to the Chinese New Year. A firing squad is the prescribed form of execution and frequently a single bullet is fired into the head of the condemned, after which his family receives a bill for the cost of the bullet. Except for Hong Kong, police are only moderately effective in providing assistance throughout the country. (Hong Kong can boast its police force is among the most effective in the world.) Most police have only a little formal education and their equipment and training are below those standards set by American enforcement agencies. Response to an emergency may take between 15 and 30 minutes. A rash of explosions in January 1999 took place in parts of central and southern China. These explosions are unusual in China, and so far have been confined to a few places such as Wuhan and Guangzhou. The risk to foreigners because of these explosions is small. Crowded public areas such as hotel lobbies, bars and restaurants, or public transportation and tourist sites are major risk areas that account for almost all of the reported crime where thefts have occurred. Travelers should avoid using unmarked taxis. Legal taxis are clearly marked, are metered, and should have the driver's identification clearly displayed. Identification cards and travel documents, such as passports and airline tickets, should be safeguarded. China has recently introduced a law that states all foreign nationals must have identifications papers on them at all times and may be stopped and asked to produce them by police on the street. Visitors should carry photocopies of these documents, as foreign nationals have been detained in the past. The photocopies should be kept in a zippered pocket or fanny pack while the originals should be kept in a hotel safe deposit box.
China has 2552 tourist hotels with 386,000 rooms, among which 1028 hotels have been star-graded according to international standards. Most of the hotels have comfortable and convenient facilities including air-conditioning and private bathrooms, Chinese and Western restaurants, coffee shops, bars, banqueting halls, conference rooms, multi-function halls, ballrooms, swimming pools, bowling alleys, beauty parlors, massage rooms, saunas, clinics and ticket booking offices. Some even include shopping and business malls, banks and post offices. Security at Chinese hotels ranges from excellent at better hotels to poor. Better hotels in China include the following: Beihai: Furama - Shangri-La Beijing: China World - Hilton - Holiday Inn Crown Plaza - Shangri-La - M?venpick - Traders - Hawaii Oriental Beijing Hotel Changchun: Shangri-La Dalian: Holiday Inn Guangzhou: Furama - Shangri-La Nanjing: Hilton Nanjing - Jinling Hotel Shanghai: Hilton Shenzhen: Forum - Golden Lustre - Shangri-La - Sunshine Tianjin: Astor Xian: Shangri-La Golden Flower.
Telephone IDD service is available and the country code is 86. The outgoing international code: 00. Internal service is often antiquated with public telephones in hotels and shops displaying telephone unit sign. It is often easier to make international phone calls from China than it is to make calls internally. Beijing now has an automatic telex service to the US and Europe. Country code: 85. Facilities are available at main and branch post offices in larger towns and cities. A growing number of hotels offer telex and fax facilities but often only incoming and rates are generally expensive. Postal service to Europe or the US takes about a week. All postal communications to China should be addressed 'People's Republic of China'.
is 220/240 volts AC, 50Hz and two-pin sockets (a few have three-pin sockets) are in use. Electricity 220 volts AC, 50Hz. Two-pin sockets and some three-pin sockets are in use. However, most 4 of 5 star hotels are wired for the use of 110 volt appliances.
A,I,G
Chinese cuisine has a very long history and is renowned all over the world. Cantonese (the style the majority of Westerners are most familiar with) is only one regional style of Chinese cooking. There are eight major schools of Chinese cuisine, named after the places where they were conceived: Anhui, Fujian, Guangdong, Hunan, Jiangsu, Shandong, Sichuan and Zhejian. For a brief appreciation of the cuisine, it is possible to break it down into four major regional categories: Northern Cuisine Beijing food has developed from the Shandong school of cuisine. Specialties:
? Peking Duck, which is roasted in a special way, and eaten in a thin pancake with cucumber and a sweet plum sauce.
? Mongolian Hotpot, a Chinese version of fondue. It is eaten in a communal style and consists of a central simmering soup in a special large round pot into which is dipped a variety of uncooked meats and vegetables, which are cooked on the spot.
? A cheap and delicious local dish is shuijiao, which is pasta-like dough wrapped round pork meat, chives and onions, similar in idea to Italian ravioli. These can be bought by the jin (pound) in street markets and small eating houses, and are a good filler if you are out all day and do not feel like a large restaurant dinner. It should, however, be noted that in the interests of hygiene, it is best to take your own chopsticks. Southern Cuisine Guangdong (Cantonese) food is famous for being the most exotic in China. The food markets in Guangzhou are a testimony to this, and the Western visitor is often shocked by the enormous variety of rare and exotic animals that are used in the cuisine, including snake, dog, turtle and wildcat. Specialties:
? Dim sum served at lunch.
? Shrimp wonton noodle soup. Eastern Cuisine Shanghai and Zhejiang cooking is rich and sweet, often pickled. Noted for seafood, hot and sour soup, noodles and vegetables. Specialties:
? La Mian (pulled noodles) served with curry beef soup.
? Xiao Long Bao (small steamer bun), pan fried pork buns eaten dipped in vinegar. Western Cuisine Sichuan and Hunan food is spicy, often sour and peppery, with specialties such as diced chicken stirred with soy sauce and peanuts, and spicy doufu (beancurd). Specialties:
? Sweet and sour chicken.
? Orange beef. National Drinks:
? One of the best-known national drinks is maotai, a fiery spirit distilled from rice wine.
? Local beers are of good quality, notably Qingdao, which is similar to German lager.
? There are now some decent wines, which are produced mainly for tourists and export, such as Qingdao white wine.
Nightlife
Visitors can follow itineraries drawn up in advance, when sampling the nightlife of the larger cities, including a selection of prearranged restaurant meals and visits to Chinese opera, Chinese state circus, ballet and theater. Local Chinese will tend to only drink socially with a formal meal so bars and nightclubs will generally only be found in the more cosmopolitan cities and major towns. Karaoke (written OK+ on Chinese signs) is a popular form of evening entertainment.
Note (a) China does not recognize dual nationality (eg US-Chinese, Canadian-Chinese). (b) Travelers are required to complete a health declaration certificate on arrival in China. HIV-positive travelers are not permitted to enter the country.
Required by all. Passport must be valid for at least six months for a single or double entry within three months of the date of visa issue; at least nine months for multiple entries within six months.
Required by all except:
(a) 1. nationals of Brunei, Japan and Singapore for stays of up to 15 days;
(b) transit passengers (except nationals of the USA, who always require a visa) continuing their journey by the same or first connecting plane to another country within 24 hours who hold valid onward documentation and do not leave the airport.
Tourist/Business/Transit (UK nationals): US$52 (single-entry); US$77 (double-entry); US$103 (multiple-entry for business visas only; six months); US$155 (multiple entry for business visas only; 12 months and two to five years). Group (at least five people): US$41 per person. Visa charges for other nationals vary; check with Embassy for further information.
Tourist, Business and Group visas are normally valid for three months from the date of issue (single and double-entry). Multiple-entry visas are normally valid for six months, 12 months or two to five years. The validity of Business visas varies. Transit visas are generally valid for up to seven days.
Consulate (or Consular section at Embassy); see Passport/Visa Information. Visas should be applied for in person at least one month before departure. Group visas will usually be obtained by the tour operator or travel agent.
(a) Completed application form. (b) One recent passport-size photo. (c) Valid passport with at least one blank page. (d) Fee (payable in cash or by postal order only). Tourist: (a)-(d) and, (e) Return airline ticket or travel information about itinerary and confirmation of hotel reservation in China. Business: (a)-(d) and, (e) Official invitation (letter/fax) from a Chinese Government department or a Government-approved company indicating duration of stay and purpose of visit (original copies must be submitted for multiple-entry visas). Student: (a)-(d) and, (e) JW_201 or JW_202 form issued by the Ministry of Education of China, and letter of admission from Chinese university/college. Group (six people or more): (a)-(d) and, (e) Confirmation letter or fax from an authorized Chinese travel company. A list of all group members should be presented in triplicate. Photocopies of all group passports with the visa form number for each member. The serial number given to group members should be listed in order on the group visa form. There should be a front page covering information about the group. Transit: (a)-(d) and, (e) Visa for the next country of destination and letter from employer (if applicable).
Three (72 hours). Two weeks for Group visas. Applications should be made at least one month in advance. A same-day service may be available at an extra cost of ?20 per person, or a 48-hour service at ?15 per person. Visas, however, cannot be issued on the same day unless the same-day airline ticket or itinerary is presented.
(a) The majority of visits to China tend to be organized through the official state travel agency CITS (China International Travel Service). This liaison with CITS is generally handled by the tour operator organizing the inclusive holiday chosen by the visitor, though it is possible for individuals to organize their own itinerary. Once the tour itinerary details have been confirmed to the visitor or visiting group, finances to cover accommodation and the cost of the tour must be deposited with CITS through a home bank. Once again, for package trips, all the necessary formalities for a visit to China can be handled by the tour operator concerned. (b) Those wishing to visit Tibet are strongly advised to join a travel group. Individual travelers need a special permit and should obtain permission to visit Tibet or Xinjiang from the following organization before applying: Tibet Tourism Office (see Passport/Visa Information). Applicants will need to supply their Chinese Visa validity dates.
Enquiries should be addressed to the Chinese Embassy.
Testing is required for foreigners planning on staying for more than 6 months. Tests are not currently required for entry or residency in Macau or Hong Kong. Anyone who is HIV positive is not allowed into China for any purpose
RMBY90. Paid in Chinese currency only. Children under 12 and transit passengers (proceeding within 24 hours) are exempt.
49-51 Portland Place, London W1B 1JL, UK
Tel: (020) 7299 8426.
Website: www.chinese-embassy.org.uk
Opening hours: Mon-Fri 0900-1230 and 1330-1700.
Consular and Visa section: 31 Portland Place, London W1B 1QD
Tel: (020) 7631 1430 (telephone enquiries: 1400-1600 only) or (09001) 880 808 (recorded visa and general information; calls cost 60p per minute).
Opening hours: Mon-Fri 0900-1200.
2300 Connecticut Avenue, NW, Washington, DC 20008, USA
Tel: (202) 328 2500.
Website: www.china-embassy.org
Visa section: Room 110, 2201 Wisconsin Avenue, NW, Washington, DC 20007, USA
Tel: (202) 338 6688.
Room 3423 Poly Plaza, 14 Dongzhimen Nandajie, Beijing 100027, People?s Republic of China
Tel: (10) 6500 1188 (ext 3423) or 6593 6538.
Website: www.tibettour.net.cn/en/
Most visits to China are trouble-free but you should be aware of the global risk of indiscriminate international terrorist attacks, which could be against civilian targets, including places frequented by foreigners.
There have been outbreaks of Avian Influenza (Bird Flu) amongst poultry in China. Since November 2005, there have been a small number of human cases in Liaoning, Guangxi, Anhui and Hunan provinces, some of which have been fatal. The individuals affected are thought to have come into contact with infected poultry before becoming sick. No evidence of human-to-human transmission is reported. The World Health Organization continues to monitor the situation.
This advice is based on information provided by the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office in the UK. It is correct at time of publishing. As the situation can change rapidly, visitors are advised to contact the following organizations for the latest travel advice:
Tel: (0845) 850 2829.
Website: www.gov.uk/foreign-travel-advice
1 Renminbi Yuan (CNY) = 10 chiao/jiao or 100 fen. Notes are in denominations of CNY100, 50, 20, 10, 5, 2 and 1, and 5, 2 and 1 chiao/jiao. Coins are in denominations of CNY1, 5 and 1 chiao/jiao and 5, 2 and 1 fen.
Import and export of local currency is limited to RMBY20000. Import of foreign currency is up to US$1000 (US$5000 for non-residents). Higher amounts should be declared upon arrival. Export of foreign currency is limited to the amount imported and declared.
Mon-Fri 0900-1200, 1400-1700.
RMBY is not traded outside China. Foreign banknotes and traveller's cheques can be exchanged at branches of The Bank of China. In hotels and Friendship Stores for tourists, imported luxury items such as spirits may be bought with Western currency. Scottish and Northern Irish banknotes cannot be exchanged.
American Express, Diners Club, Eurocard/MasterCard and Visa are widely accepted in major provincial cities in designated establishments. However, the availability of ATMs is often limited, and the acceptance of credit cards often unlikely away from the major cities.
To avoid additional exchange rate charges, travelers are advised to take traveller's cheques in US Dollars.
| City/Region | City/Area code | Followed by |
|---|---|---|
| Akesu, XJ | (0)997 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Alashanzuoqi, NM | (0)483 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Aletai, XJ | (0)906 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Ankang, SN | (0)915 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Anqing, AH | (0)556 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Anshan, LN | (0)412 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Anshun, GZ | (0)853 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Anyang, HEN | (0)372 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Atushi, XJ | (0)908 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Baicheng, JL | (0)436 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Baise, GX | (0)776 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Baishan, JL | (0)439 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Baiyin, GS | (0)943 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Bange, XZ | (0)8067 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Baoding, HEB | (0)312 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Baoji, SN | (0)917 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Baoshan, YN | (0)875 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Baotou, NM | (0)472 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Bazhong, SC | (0)827 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Beihai, GX | (0)779 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Beijing, BJ | (0)10 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Bengbu, AH | (0)552 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Benxi, LN | (0)414 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Bijie, GZ | (0)857 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Binzhou, SD | (0)543 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Bole, XJ | (0)909 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Cangzhou, HEB | (0)317 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Changchun, JL | (0)431 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Changde, HN | (0)736 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Changdu, XZ | (0)895 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Changji, XJ | (0)994 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Changsha, HN | (0)731 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Changzhi, SX | (0)355 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Changzhou, JS | (0)519 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chaohu, AH | (0)565 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chaoyang, GD | (0)754 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chaoyang, LN | (0)421 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chaozhou, GD | (0)768 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chengde, HEB | (0)314 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chengdu, SC | (0)28 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Chenzhou, HN | (0)735 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chifeng, NM | (0)476 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chizhou, AH | (0)566 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chongqing, CQ | (0)23 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Chuxiong, YN | (0)878 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Chuzhou, AH | (0)550 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Dali, YN | (0)872 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Dalian, LN | (0)411 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Dandong, LN | (0)415 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Daqing, HL | (0)459 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Datong, SX | (0)352 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Dazhou, SC | (0)818 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Delingha, QH | (0)977 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Deyang, SC | (0)838 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Dezhou, SD | (0)534 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Dingxi, GS | (0)932 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Dongguan, GD | (0)769 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Dongsheng, NM | (0)477 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Dongying, SD | (0)546 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Duyun, GZ | (0)854 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Enshi, HB | (0)718 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Ezhou, HB | (0)711 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Fangchenggang, GX | (0)770 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Foshan, GD | (0)757 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Fushun, LN | (0)413 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Fuxin, LN | (0)418 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Fuyang, AH | (0)558 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Fuzhou, FJ | (0)591 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Fuzhou, JX | (0)794 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Ganzhou, JX | (0)797 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| GeEr, XZ | (0)897 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| GeErmu, QH | (0)979 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Gejiu, YN | (0)873 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Gonghe, QH | (0)974 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| GuangAn, SC | (0)826 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Guangyuan, SC | (0)839 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Guangzhou, GD | (0)20 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Guilin, GX | (0)773 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Guiyang, GZ | (0)851 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Guyuan, NX | (0)954 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Haikou, HQ | (0)898 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Hailaer, NM | (0)470 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Haiyan, QH | (0)970 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hami, XJ | (0)902 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Handan, HEB | (0)310 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hangzhou, ZJ | (0)571 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Hanzhong, SN | (0)916 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Harbin, HL | (0)451 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Hebi, HEN | (0)392 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hechi, GX | (0)778 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hefei, AH | (0)551 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hegang, HL | (0)468 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Heihe, HL | (0)456 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hengshui, HEB | (0)318 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hengyang, HN | (0)734 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hetian, XJ | (0)903 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Heyuan, GD | (0)762 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Heze, SD | (0)530 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hezuo, GS | (0)941 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huaibei, AH | (0)561 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huaihua, HN | (0)745 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huainan, AH | (0)554 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| HuaiYin, JS | (0)517 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huangchuan, HEN | (0)397 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huanggang, HB | (0)713 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huangshan, AH | (0)559 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huangshi, HB | (0)714 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huhehaote, NM | (0)471 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huizhou, GD | (0)752 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huludao, LN | (0)429 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Hunchun, JL | (0)440 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Huzhou, ZJ | (0)572 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jiagedaqi, HL | (0)457 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jiali, XZ | (0)8063 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Jiamusi, HL | (0)454 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| JiAn, JX | (0)796 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jiangmen, GD | (0)750 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jiaozuo, HEN | (0)391 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jiaxing, ZJ | (0)573 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jieyang, GD | (0)663 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jilin, JL | (0)432 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jinan, SD | (0)531 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Jinchang, GS | (0)935 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jincheng, SX | (0)356 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jingdezhen, JX | (0)798 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jinghong, YN | (0)691 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jingmen, HB | (0)724 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jingzhou, HB | (0)716 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jinhua, ZJ | (0)579 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jining, NM | (0)474 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jining, SD | (0)537 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jinzhou, LN | (0)416 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jishou, HN | (0)743 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jiujiang, JX | (0)792 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jiuquan, GS | (0)937 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Jixi, HL | (0)467 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Kaifeng, HEN | (0)378 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Kaili, GZ | (0)855 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Kalamayi, XJ | (0)990 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Kangding, SC | (0)836 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Kashi, XJ | (0)998 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| KuErle, XJ | (0)996 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Kuitun, XJ | (0)992 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Kunming, YN | (0)871 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Laiwu, SD | (0)634 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Langfang, HEB | (0)316 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Lanzhou, GS | (0)931 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Leshan, SC | (0)833 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Lhasa, XZ | (0)891 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Lianyungang, JS | (0)518 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Liaocheng, SD | (0)635 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Liaoyang, LN | (0)419 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Liaoyuan, JL | (0)437 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Lijiang, YN | (0)888 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Lincang, YN | (0)883 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Linfen, SX | (0)357 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Linhe, NM | (0)478 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Linxia, GS | (0)930 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Linyi, SD | (0)539 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Linzhi, XZ | (0)894 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Lishi, SX | (0)358 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Lishui, ZJ | (0)578 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| LiuAn, AH | (0)564 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Liuku, YN | (0)886 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Liupanshui, GZ | (0)858 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Liuzhou, GX | (0)772 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Longyan, FJ | (0)597 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Loudi, HN | (0)738 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Luohe, HEN | (0)395 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Luoyang, HEN | (0)379 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Luxi, YN | (0)692 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Luzhou, SC | (0)830 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| MaAnshan, AH | (0)555 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| MaErkang, SC | (0)837 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Maoming, GD | (0)668 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Maqin, QH | (0)975 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Meihekou, JL | (0)448 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Meizhou, GD | (0)753 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Mianyang, SC | (0)816 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Mudanjiang, HL | (0)453 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Naidong, XZ | (0)893 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Nanchang, JX | (0)791 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Nanchong, SC | (0)817 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Nanjing, JS | (0)25 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Nanning, GX | (0)771 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Nanping, FJ | (0)599 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Nantong, JS | (0)513 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Nanyang, HEN | (0)377 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Naqu, XZ | (0)896 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Neijiang, SC | (0)832 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Nierong, XZ | (0)8065 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Nima, XZ | (0)8081 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Ningbo, ZJ | (0)574 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Ningde, FJ | (0)593 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Panjin, LN | (0)427 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Panzhihua, SC | (0)812 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| PingAn, QH | (0)972 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Pingdingshan, HEN | (0)375 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Pingliang, GS | (0)933 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Pingxiang, JX | (0)799 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Pulan, XZ | (0)8060 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Putian, FJ | (0)594 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Puyang, HEN | (0)393 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Qingdao, SD | (0)532 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Qingyuan, GD | (0)763 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Qinhuangdao, HEB | (0)335 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Qinzhou, GX | (0)777 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Qiqihar, HL | (0)452 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Qitaihe, HL | (0)464 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Quanzhou, FJ | (0)595 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Qujing, YN | (0)874 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Quzhou, ZJ | (0)570 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Rikaze, XZ | (0)892 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Rizhao, SD | (0)633 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Sanmenxia, HEN | (0)398 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Sanming, FJ | (0)598 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shanghai, SH | (0)21 | + 8/10 digit subscriber nr |
| Shangqiu, HEN | (0)370 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shangrao, JX | (0)793 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shangzhou, SN | (0)914 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shanwei, GD | (0)660 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shaoguan, GD | (0)751 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shaoxing, ZJ | (0)575 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shaoyang, HN | (0)739 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shenyang, LN | (0)24 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Shenzha, XZ | (0)8068 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Shenzhen, GD | (0)755 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Shihezi, XJ | (0)993 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shijiazhuang, HEB | (0)311 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Shiyan, HB | (0)719 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shizuishan, NX | (0)952 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shuanghu, XZ | (0)8070 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Shuangyashan, HL | (0)469 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Shuozhou, SX | (0)349 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Simao, YN | (0)879 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Siping, JL | (0)434 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Songyuan, JL | (0)438 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Suihua, HL | (0)455 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Suining, SC | (0)825 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Suizhou, HB | (0)722 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Suoxian, XZ | (0)8078 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Suqian, JS | (0)527 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Suzhou, AH | (0)557 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Suzhou, JS | (0)512 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Tacheng, XJ | (0)901 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| TaiAn, SD | (0)538 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Taiyuan, SX | (0)351 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Taizhou, JS | (0)523 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Taizhou, ZJ | (0)576 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tangshan, HEB | (0)315 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tianjin, TJ | (0)22 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Tianshui, GS | (0)938 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tieling, LN | (0)410 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tongchuan, SN | (0)919 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tonghua, JL | (0)435 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tongliao, NM | (0)475 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tongling, AH | (0)562 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tongren, GZ | (0)856 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tongren, QH | (0)973 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Tulufan, XJ | (0)995 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Urumchi, XJ | (0)991 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Weifang, SD | (0)536 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Weihai, SD | (0)631 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Weinan, SN | (0)913 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Wenshan, YN | (0)876 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Wenzhou, ZJ | (0)577 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Wudu, GS | (0)939 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Wuhai, NM | (0)473 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Wuhan, HB | (0)27 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Wuhu, AH | (0)553 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Wulanhaote, NM | (0)482 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Wuxi, JS | (0)510 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Wuzhong, NX | (0)953 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Wuzhou, GX | (0)774 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xiamen, FJ | (0)592 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| XiAn, SN | (0)29 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Xiangfan, HB | (0)710 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xiangtan, HN | (0)732 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xianning, HB | (0)715 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xiantao, HB | (0)728 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xianyang, SN | (0)910 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xiaogan, HB | (0)712 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xichang, SC | (0)834 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xifeng, GS | (0)934 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xilinhaote, NM | (0)479 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xingtai, HEB | (0)319 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xingyi, GZ | (0)859 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xining, QH | (0)971 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xinxiang, HEN | (0)373 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xinyang, HEN | (0)376 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xinyu, JX | (0)790 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xinzhou, SX | (0)350 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xuancheng, AH | (0)563 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xuchang, HEN | (0)374 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Xuzhou, JS | (0)516 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| YaAn, SC | (0)835 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| YanAn, SN | (0)911 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yancheng, JS | (0)515 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yangjiang, GD | (0)662 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yangquan, SX | (0)353 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yangzhou, JS | (0)514 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yanji, JL | (0)433 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yantai, SD | (0)535 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yibin, SC | (0)831 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yichang, HB | (0)717 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yichun, HL | (0)458 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yichun, JX | (0)795 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yinchuan, NX | (0)951 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yingkou, LN | (0)417 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yingtan, JX | (0)701 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yining, XJ | (0)999 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yiyang, HN | (0)737 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yongzhou, HN | (0)746 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yuci, SX | (0)354 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yueyang, HN | (0)730 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yulin, GX | (0)775 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yulin, SN | (0)912 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yuncheng, SX | (0)359 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yunfu, GD | (0)766 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yushu, QH | (0)976 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Yuxi, YN | (0)877 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zaozhuang, SD | (0)632 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhada, XZ | (0)8071 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhangjiajie, HN | (0)744 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhangjiakou, HEB | (0)313 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhangye, GS | (0)936 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhangzhou, FJ | (0)596 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhanjiang, GD | (0)759 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhaoqing, GD | (0)758 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhaotong, YN | (0)870 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhengzhou, HEN | (0)371 | + 8 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhenjiang, JS | (0)511 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhongba, XZ | (0)8029 | + 4 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhongdian, YN | (0)887 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhongshan, GD | (0)760 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhoukou, HEN | (0)394 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhoushan, ZJ | (0)580 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhuhai, GD | (0)756 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhumadian, HEN | (0)396 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zhuzhou, HN | (0)733 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zibo, SD | (0)533 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zigong, SC | (0)813 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
| Zunyi, GZ | (0)852 | + 7 digit subscriber nr |
Good dental care is available in the larger cities. Avoid dental treatment elsewhere in china as the standard of care cannot be guaranteed
Only purchase medication from the larger pharmacies in the cities, which stock internationally produced drugs. Avoid provincial pharmacies which may sell locally made products.
There is a shortage of blood products in China and what supplies there are may not be adequately screened, therefore blood supplies should be considered as unsafe.
The quality of medical care in China varies. Competent, trained doctors and nurses are available in major metropolitan centers, but many do not speak English. Hospital accommodations are spartan, and medical technology is not up-to-date. Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for health services and may not accept checks or credit cards.
Recent medical and dental exams should ensure that the traveler is in good health. Carry appropriate health and accident insurance documents and copies of any important medical records. Bring an adequate supply of all prescription and other medications as well as any necessary personal hygiene items, including a spare pair of eyeglasses or contact lenses if necessary. Drink only bottled beverages (including water) or beverages made with boiled water. Do not use ice cubes or eat raw seafood, rare meat or dairy products. Eat well-cooked foods while they are still hot and fruits that can be peeled without contamination. Avoid roadside stands and street vendors. Swim only in well-maintained, chlorinated pools or ocean water known to be free from pollution; avoid freshwater lakes, streams and rivers. Wear clothing which reduces exposed skin and apply repellents containing DEET to remaining areas. Sleep in well-screened accommodations. Carry anti-diarrheal medication. Reduce problems related to sun exposure by using sunglasses, wide-brimmed hats, sunscreen lotions and lip protection.
A new strain of cholera (Bengal cholera) has appeared in western China. Disease caused by this new strain is characterized by extremely rapid onset of severe symptoms. The current cholera vaccine affords no protection against this new strain; therefore, particular caution should be taken with food, beverages and personal hygiene. Persons becoming ill should seek immediate medical care and rehydration therapy. AIDS occurs. Blood supply may not be adequately screened and/or single-use, disposable needles and syringes may be unavailable. When possible, travelers should defer medical treatment until reaching a facility where safety can be assured. (According to press reports, a long-term AIDS prevention program, including blood screening and public education, has been launched to combat the spread of the disease. The significant increase in cases is being blamed on growing prostitution and drug use, as well as poor hygiene practices by some health providers, who now may face criminal prosecution if HIV is found in the blood supply.) The blood type of the general Asian populace is Rh positive; Rh negative blood may be difficult to obtain. Because of the prevailing dust, and the burning of soft coal during the winter, Beijing has a high rate of pollution, and thus causes many bronchial/sinus ailments. Rabid dogs present a problem throughout China. Reports indicate that as many as one million people are bitten by rabid dogs each year and that 5,000 of those victims die (the high mortality rate is attributed to a scarcity of rabies vaccine in rural areas where bite victims cannot be treated in time). Measures taken to control the number of dogs have not met with substantial results. While pet canines are banned in China's crowded cities without police permission, the rules are often unenforced, and the canine population is now estimated at 100 million. Travelers should remain well clear of roaming dogs and to seek immediate medical attention if injured by a dog. Persons electing to see China via riverboat should choose modern ships for sanitary reasons since many older boats use untreated river water for washing dishes and in bathrooms - thus increasing the risk of illnesses such as traveler's diarrhea and schistosomiasis. Sunlight is intense at Tibet's high elevations, and travelers there should bring sun screen. Also intense is the dust level in Lhasa, and a face mask is suggested. Respiratory problems are common; thus, antihistamines and cough syrup are recommended items. Other practical items include tissues, toilet tissue, and wet wipes. Virtually all of the Tibetan Autonomous Region, much of Qinghai and Xinjiang, and parts of Sichuan, Yannan, and Gansu are above 13,000 feet (4,000 meters) in altitude. Some main roads in Tibet, Qinghai, and Xinjiang go above 17,000 feet (5,200 meters), where available oxygen is only half that available at sea level. Conditions in Tibet are primitive and travel there can be particularly arduous. Medical facilities are practically nonexistent. Many otherwise healthy visitors to these high altitude areas of Tibet may suffer severe headaches, nausea, dizziness, shortness of breath, or a dry cough. These symtoms usually disappear after a few days of acclimatization. However, if they do not, sufferers should descend to a lower altitude, or seek medical assistance. Visitors with respiratory or cardiac problems should avoid such high altitudes and consult a physician before making the trip. No Western brand-name drugs or non-prescription medicines are available locally, although some Chinese equivalents are found at modest prices.
Cholera: Although limited in effectiveness, vaccination may be appropriate for persons living and/or working in less than sanitary conditions for more than 3 months where medical facilities are unavailable. Vaccination may also be appropriate for travelers with impaired gastric defenses who are planning an extended visit or being exposed to unsanitary conditions. Vaccination is not advised for pregnant women, infants younger than 6 months old, or persons with a history of severe reaction to the vaccine. Hepatitis A: Consider active immunization with hepatitis A vaccine or passive immunization with immune globulin (IG) for all susceptible travelers. Especially consider choosing active immunization for persons planning to reside for a long period or for persons who take frequent short-term trips to risk areas. The importance of protection against hepatitis A increases as length of stay increases. It is particularly important for persons who will be living in or visiting rural areas, eating or drinking in settings of poor or uncertain sanitation, or who will have close contact with local persons (especially young children) in settings with poor sanitary conditions. Hepatitis B: Vaccination is advised for health care workers, persons anticipating direct contact with blood from or sexual contact with inhabitants, and persons planning extended stays of 6 months or greater (especially those who anticipate using local health care facilities, staying in rural areas, or having intimate contact with the local population). Japanese Encephalitis: Vaccination is not routinely recommended for travelers visiting urban areas only. However, consider vaccination if staying a month or more during transmission season (May to September in north; April to October in south) if travel includes rural areas. Also consider if staying less than 30 days during these periods and at high risk (in case of epidemic outbreak or extensive outdoor exposure in rural areas). No cases have been reported in Xizang (Tibet), Xinjiang and Qinghai provinces. Southern risk area consists of Yunnan, Guangxi and Guangdong provinces, plus the southern portions of Sichuan, Guizhou, Hunan, Jiangxi and Fujian provinces. Polio: A one-time booster dose is recommended for travelers who have previously completed a standard course of polio immunization. Refer to CDC guidelines for vaccinating unimmunized or incompletely immunized persons. Pregnancy is a relative contraindication to vaccination; however, if protection is needed, either IPV or OPV may be used, depending on preference and time available. Rabies: Preexposure vaccination should be considered for persons staying longer than 30 days who are expected to be at risk to bites from domestic and/or wild animals (particularly dogs), or for persons engaged in high risk activities such as spelunking or animal handling. Need for vaccination is more important if potential exposure is in rural areas and if adequate postexposure care is not readily available. Typhoid: Vaccination should be considered for persons staying longer than 3 weeks, adventurous eaters, and those who will venture off the usual tourist routes into small cities, villages and rural areas. Importance of vaccination increases as access to reasonable medical care becomes limited. Contraindications depend on vaccine type. Note: All routine vaccines (such as DTP or Td, Hib, MMR, polio, varicella, influenza and pneumococcal) should be kept up-to-date as a matter of good health practice unrelated to travel.
Insect-borne illness: Dengue fever - occurs Dengue hemorrhagic fever - occurs Encephalitis (Japanese type) - common (hyperendemic in southern areas, endemic with periodic epidemics in northern areas) Encephalitis (tick-borne) - occurs Filariasis (Bancroftian type) - occurs Filariasis (Malayan type) - occurs Hemorrhagic fever (with renal syndrome) - occurs Leishmaniasis (visceral) - occurs Malaria - occurs Plague - occurs Typhus (mite-borne) - occurs in southern areas Food-borne and water-borne illness: diseases such as the diarrheal diseases and hepatitis are common. Brucellosis - occurs Cholera - occurs Clonorchiasis (oriental liver fluke) - occurs Fasciolopsiasis (giant intestinal fluke) - occurs Leptospirosis - occurs Paragonimiasis (oriental lung fluke) - occurs Schistosomiasis - occurs in many watercourses of southeastern and eastern China along the Changjiang (Yangtze) Valley and its tributaries (also known as the "lake country") Typhoid - occurs Other hazards: Diseases such as measles and diphtheria are commonly reported, and cases of polio still occur regularly. Influenza risk extends from November to April. Trachoma - occurs Tuberculosis - common (incidence is 55 times the rate in the United States)
AIDS: According to the Department of State, testing is required for those staying more than 6 months. Foreign test results are accepted under certain conditions. Contact China's embassy for details. Yellow fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required from travelers coming from infected areas.
No recent disease outbreaks
| Name | Address |
|---|---|
| Adventist Hospital | 40 Stubbs Road Hong Kong SAR |
| American-Sino Ob/Gyn Service | 16th Floor, New Blue Building Huashan Hospital 12 Wulumuqi Zhong Road Shanghai 200040 |
| American-Sino Ob/Gyn Services - Beijing | 5th Floor, 218 Xiaoguan Beili Anwai Chaoyang District Beijing 100029 |
| Arrail Dental Beijing Pediatric Center | 208 CITIC Building 19 Jianguomenwai Street Beijing 100004 |
| Arrail Dental Implant Center | 201 The Exchange - Beijing 118 Yi Jianguolu Beijing 100022 |
| Arrail Dental Somerset Fortune Garden Clinic | 1st Floor, Somerset Fortune Garden 46 Liang Ma Qiao Beijing 100016 |
| Arrail Dental Zhongguancun Clinic | 308 Raycom Info Tech Park Tower A 2 Science Institute South Road Handian District Beijing 100080 |
| Bayley and Jackson Medical Centre (Out Patient Services Only) | No.7 Ritan Dong Lu Chaoyang District Beijing 100020 |
| Beijing International (SOS) Clinic | Building C BITIC Jing Yi Building No.5 Sanlitun Xiwujie Chaoyang District Beijing 100027 |
| Beijing New World Eaton Medical Center | Level 5F, Beijing New World Shopping Centre 3 Chong Wen Men Wai Street Beijing 100062 |
| Beijing United Family Clinic -Shunyi | Pinnacle Plaza, Unit #818 Tian Zhu Real Estate Development Zone Shunyi District Beijing 101312 |
| Beijing United Family Health & Wellness Center - Jianguomen | Basement 1, Beijing International Club Hotel (The St. Regis Hotel, Beijing) 21 Jiangguomenwai Dajie, B1 The St. Regis Residence Beijing |
| Beijing United Family Hospital and Clinics | 2 Jiangtai Lu Chaoyang District Beijing 100016 |
| Beijing Vista Clinic | Kerry Center Shopping Mall No. 1 Guanghua Road Chaoyang District Beijing 100020 |
| Cidi Dental Clinic | Room 706-708, 495 Jiang Ning Road (near Kang Ding Road) Boo Hong Mansion Shanghai |
| Clifford Hospital | Shiguang Road Pangyu Guangdong |
| DDS Hong Qiao Dental Clinic | Suite 2, 85 Jin Hui Road (near French and German School) Shanghai 201100 |
| DDS PuDong (Lujiazui) Dental Clinic | B1-F POS Plaza Building 1600 Century Avenue LuJiaZui of PuDong Shanghai 200122 |
| Dr. Anderson & Partners General Medical Clinic | Room 1001 Block D New Century Plaza 48 Xing Yi Road Hong Qiao |
| Dr. Harriet Jin's Dental Surgery | Room 1904 Hui Yin Plaza (South Building) (immediately next to Grand Gateway) 2088 Hua Shan Road Shanghai 200030 |
| Dr. Lu Dental Clinic | Room 603-604 6/F Metro Plaza 183 Tian He Bei Road Guangzhou |
| Eur Am International Medical Center | 1/F North Tower, Ocean Pearl Building, No19 Hua Li Lu Zhu Jiang New City Guangzhou 510623 |
| Fudan Vision Medical and Healthcare Centre | 3rd floor Silver Towers No. 228 South Xizang Road Shanghai 200021 |
| Global Doctor Chengdu Clinic | Ground Floor of Ting Tao Yuan PanGu Garden No. 21 Ren Min Nan Lou Si Duan Chengdu 610041 |
| Global Doctor Chengdu Clinic | Ground Floor of Ting Tao Yuan PanGu Garden No. 21 Ren Min Nan Lou Si Duan Chengdu 610041 |
| Global Doctor Chongqing Clinic | Room 701, Business Tower, Hilton Chongqing No. 139 Zhong Shan san Lu, Yu Zhong District Chongqing 400015 |
| Global Doctor Chongqing Clinic | Room 701, Business Tower, Hilton Chongqing No. 139 Zhong Shan san Lu, Yu Zhong District Chongqing 400015 |
| Global Doctor Guangzhou Clinic | Guangzhou City No. 1 People's Hospital Out-Patient Department - 7th Floor Pan Fu Lu 1 Guangzhou 510180 |
| Global Doctor Guangzhou Clinic | Guangzhou City No. 1 People's Hospital Out-Patient Department - 7th Floor Pan Fu Lu 1 Guangzhou 510180 |
| Global Doctor Shenyang Clinic | De Ji Hospital 54 Bang Jiang Road Dadong District Shenyang 110042 |
| Global Doctor Shenyang Clinic | De Ji Hospital 54 Bang Jiang Road Dadong District Shenyang 110042 |
| Global HealthCare Clinic | Shanghai Kerry Centre, Room 301 1515 Nanjing West Road Jing An District Shanghai 200040 |
| Guang Ci Hospital | c/o Rui Jin Hospital, Building 38, 197 Rui Jin Er Road, Shanghai Shanghai 200025 |
| Guangdong Concord Medical Centre | Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital 9th Floor, Dr. Y.T. Fok Heart Centre No. 96 Dong Chuan Road Guangzhou City 510100 Guangdong Province |
| Guangzhou Can Am International Medical Center | (IMC) 5/F Garden Tower Garden Hotel 368 Huanshi Dong Road Guangzhou 510064 |
| Guangzhou Can Am International Medical Centre | 5/F Garden Tower, Garden Hotel 368 Huanshi Dong Lu Guangzhou 510064 |
| Hong Kong Baptist Hospital | 222 Waterloo Road Kowloon Tong Hong Kong SAR |
| Hong Kong Central Hospital | 1B Lower Albert Road Central Hong Kong SAR |
| Hong Kong International Medical Clinic - Beijing | 9/F Office Tower, Hong Kong Macau Center 2 Chao Yang Men Bei Da Jei Road Chao Yang District Beijing 100027 |
| Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital Ltd | 2 Village Road Happy Valley HONG KONG SAR |
| Hong Kong Surgical Specialists | 715 Jardine House Hong Kong SAR |
| International Medical Center - Beijing | Office Building S106, Kempinski Hotel Beijing Lufthansa Centre No. 50 Liang Maqiao Road Beijing 100016 |
| International Medical Center (IMC) | 4/F Shangri-La Hotel Putong Shanghai |
| International Peace Maternity & Child Health Hospital of the | VIP 6th Floor 1961 Huashan Road Shanghai 200030 |
| International SOS Nanjing Clinic | Ground Floor Nanjing Hilton Hotel, 319 Zhong Shan Dong Lu, Nanjing Nanjing Jiangsu 210016 |
| Kiang Wu Hospital | Estrada Coelho do Amaral Macau SAR |
| Ma On Shan Polyclinic | (Union Hospital Polyclinic) Shop No. 11-12, G/F Sunshine Bazaar Ma On Shan Hong Kong SAR |
| Matilda International Hospital | 41 Mount Kellett Road The Peak Hong Kong SAR |
| North American International Hospital | 419 He Fang Street Hangzhou Zhejiang Province 310002 |
| Peking Union Medical College Hospital | No.1 Shuaifuyuan Wangfujin Dongcheng District Beijing Beijing 100730 |
| Peking Union Medical College Hospital (PUMCH) | (Foreign Patient Department) 1 Shuaifuyuan Dongcheng District Beijing 100730 |
| Raffles Central Medical Centre | 902 Bank of America Tower 12 Harcourt Road Central Hong Kong SAR |
| Ruijin Hospital - Guang Ci | Foreigners Unit affiliated to World Link Medical Centers 197 Ruijin Er Road Luwan Shanghai |
| SDM 21st Century Hotel Dental Clinic | FC222, 21st Century Hotel 40 Liang Maqiao Road Chaoyang District Beijing 100016 |
| SDM China World Trade Center Dental Clinic | 210 China World Shopping Mall (Beside Skating-Rink) 1 Jian Guo Men Wai Avenue Beijing 100004 |
| SDM Gu Rui Dental Clinic | 23 Longcao Road Xuhui District Shanghai 200233 |
| SDM Mei Ke Dental Clinic | 33 Shuicheng.S Road Shanghai 201103 |
| SDM Sunshine Plaza Dental Clinic | F-0186B, Sunshine Plaza 68 Anli Road Chaoyang District Beijing 100026 |
| Shanghai Arrail Dental Clinic | 204 Lippo Plaza 222 Huai Hai Zhong Road Shanghai 200021 |
| Shanghai Can Am International Medical Center | 20/F 966 Huai Hai Middle Road (Xu Hui Central District Hospital) Shanghai |
| Shanghai Chang Ning District Central Hospital | 1111 Xianxia Lu Chang Ning District Shanghai |
| Shanghai Concord Medical Specialists Center | Room 602, Jin Tai Office Building No. 58 Mao Nan Road Shanghai 200020 |
| Shanghai East International Medical Center | 551 South Pudong Road Pudong Shanghai 200120 |
| Shanghai Hua Shan Hospital Worldwide | 15,16F, 12 Ulumuqi Rd,Shanghai (inpatient wards) 1F,1068 Chang Le Rd (outpatient clinic) 430 Huashan Rd (fever clinic) VIP outpatient clinic Shanghai Shanghai 200040 |
| Shanghai United Family Clinic - Minhang | Shanghai Racquet Club, Club House Lane 555 Jinfeng Lu Minhang District Shanghai 201107 |
| Shanghai United Family Hospital | 1139 Xian Xia Lu Changning District Shanghai 200336 |
| Shekou International SOS Clinic | G/F CMIT Building, No. 9 Industrial Road South, Shekou Shenzhen Guangdong 518067 |
| Shenyang International Travel Health Centre | 433 Da nan Street Shen He District Shenyang 110016 |
| Shenzhen Arrail Dental Clinic | Unit 2 G3/F, Office Tower Shunhing Square Di Wang Commercial Center 5002 Shen Nan Zhong Road Shenzhen 518008 |
| Sino United Health American International Center | at Shanghai Center Room 601 (West Wing) 1376 NanJing Road West Shanghai 200041 |
| Sino-German Policlinic | Landmark Tower, Room B-1 8 North Dong San Huan Road Chao Yang District Beijing 100004 |
| Sino-Japan Friendship Hospital | Yinghua East Road Hepingli International Medical Dept. Beijing Beijing 100029 |
| St. Paul's Hospital | 2 Eastern Hospital Road Causeway Bay Hong Kong Island Hong Kong SAR |
| St. Teresa's Hospital | 327 Prince Edward Road Kowloon Hong Kong SAR |
| Tianjin International SOS Clinic | Ground Floor of Sheraton Tianjin Hotel Apartment Building Zi Jin Shan Road He Xi District Tianjin Tianjin Tianjin 300074 |
| Tongji Medical University Hospital | 13 Hangkong Road Wuhan Hubei |
| Tseung Kwan O Polyclinic (Union Hospital Polyclinic) | Shop No. 210, Level 2, Metro City Plaza III Tseung Kwan O Hong Kong SAR |
| Union Hospital | 18 Fu Kin Street Tai Wai New Territories Hong Kong SAR |
| World Link - Hong Qiao Medical and Dental Center | Mandarine City - Suite 30 788 Hong Xu Lu Shanghai 201103 |
| World Link - Hong Qiao Medical Center | 2258 Hong Qiao Lu (nr. Hong Qiao Marriott Hotel and historic Kung Villa) Shanghai 201103 |
| World Link - Jin Qiao Medical and Dental Center | 51 Hongfeng Lu Jin Qiao Pudong Shanghai 2011103 |
| World Link - Specialty and Inpatient Center | 170 Danshui Lu, 3rd Floor (nr. Corner of Danshui Lu and Xinye Lu, nr. Xintiandi) Shanghai 200020 |
| Xinjiang International Travel Health-Care | 6B Beijing Nan Lu Urumqi Xinjiang 830011 |
China's media are tightly controlled by the country's leadership. The industry has been opened up in the areas of distribution and advertising but not in Editorial content. Access to foreign news providers is limited and re-broadcasting and the use of satellite receivers is restricted; shortwave radio broadcasts are jammed and websites are blocked. In general, the press report on corruption and inefficiency among officials, but the media avoid criticism of the Communist Party's monopoly on power. Hong Kong so far has retained its Editorially free media. Each city has its own newspaper, usually published by the local Government, as well as a local Communist Party daily. Agreements are in place which allow selected channels - including stations run by AOL Time Warner, News Corp and the Hong Kong-based Phoenix TV - to transmit via cable in Guangdong province. In exchange, Chinese Central TV's English-language network is made available to satellite TV viewers in the US and UK. Beijing says it will only allow relays of foreign broadcasts which do not threaten "national security" or "political stability". All foreign-made TV programs will be subject to approval before broadcast.
Press: The main English-language daily is the China Daily. There is also the weekly news magazine Beijing Review, with editions in English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish. National newspapers include The People's Daily and The Worker?s Daily, with many provinces having their own local dailies as well. News agencies include the state-run Xinhua and Zhongguo Xinwen She (aimed mainly at overseas Chinese nationals).
TV: Chinese Central TV (CCTV) is a state-run national broadcaster, with networks that include English-language CCTV-9.
Radio: China National Radio is state-run; China Radio International is a state-run external broadcaster with programd in more than 40 languages.